International experts for software quality cooperate in the GFFT Software Lab. Qentinel, a leading specialist in test automation, and the GFFT (Society for the Promotion of Research Transfer) are launching a consortium project on "Software Testing in the Automotive Cloud" in 2021. The aim is to develop practice-oriented solutions for the special challenges of connected driving. Interested software testers, software developers and automotive engineers are cordially invited to exchange personal experiences. Several (online) workshops are planned for 2021, focusing around Android Automotive, Adaptive Autosar and Test Automation in the Cloud.
1) Android Automotive - Quality assurance for the operating system of the future
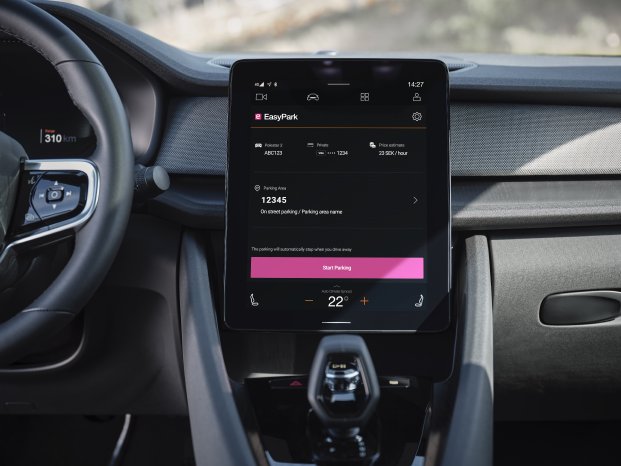
One focus of the consortium project is the Android Automotive operating system, which OEMs such as Volvo already use in their premium models. It enables innovative applications such as driverless automated parking in car parks, but also requires particularly powerful testing methods. In the consortium project, Qentinel will demonstrate how to quickly create and efficiently execute automated software tests for Android Automotive applications.
Background: A flourishing ecosystem is currently emerging around Android Automotive. In the connected car, the operating system of the touchscreen display is the interface between driver, vehicle, networks, data services and service providers. And just as with smartphones, only two or three operating systems will be at the centre of a mega-market in connected cars. Currently, Google's parent company Alphabet is ahead with Android Automotive. It runs, for example, in the new model of Volvo's premium brand Polestar. The advantage for customers: They get a premium infotainment system with the familiar usability of their smartphone as well as a rapidly growing range of special apps. Car manufacturers can significantly reduce their development costs by using Android Automotive. And service providers gain another sales channel for their services and a market for new digital business models.
2) Adaptive AutoSar - testing in the new industry standard of connected driving.
The international AutoSar consortium is an association of leading car manufacturers, suppliers and software developers. The Adaptive AutoSar standard defines the basics of quality assurance for over-the-air software updates and for connected to highly automated driving. As vehicle software becomes increasingly complex, software testing is also particularly demanding. Qentinel shows how development speed and test efficiency can be increased through automation.
Background: The car of the future will not only be low-emission, but also a hyper-networked high-performance computer on wheels. Studies predict that 500 million connected cars will be rolling on the roads in 2025. Today, modern cars already collect up to 25 GB of data per driving hour and their computers contain over 100 million lines of code - valuing one line of code at a cost of around Euro 10, this means an investment of Euro 1 billion in the software of a new vehicle alone. Future vehicles, however, will contain 200 to 300 lines of code. 80% of the value creation of the automotive sector will then be accounted for by software and digital services. Many of them are loaded "over the air" and regularly updated, just like a smartphone. This requires particularly powerful, agile and flexible quality assurance via the cloud.
3) Agile test automation - what opportunities does the cloud offer OEMs and suppliers?
While agile methods such as DevOps and cloud-based solutions are becoming established in the software industry, this is still unusual in the automotive industry. However, due to the increasing networking of software and hardware, OEMs and suppliers need to harmonize their methods and platforms with the software world. In a workshop, Qentinel shows how to connect virtual software testing robots and physical hardware testing robots via the cloud. For example, a human's input on the touchscreen display in the vehicle can be simulated as part of automated tests. In the process, the hardware engineers in the car factory and the software engineers in the development centre work together efficiently and in a time-saving manner via the cloud.
Background: Testing is becoming a bottleneck. If software developers want to further accelerate their release tempo, they must switch to agile methods such as DevOps and cloud-based platforms - and testing with them. At the same time, more and more externally networked systems need to be considered alongside those embedded in the vehicle. This creates a complexity of quality requirements for the software that can only be managed by harmonizing procedures through new standards, accelerating testing through automation and connecting the testing infrastructure in the cloud.