Goals of the pilot implementation
The project has two key goals: firstly, creating a specification for packaging machines in accordance with the packaging machine language PackML. PackML is a guideline for open, modular automation architectures issued by the OMAC user group (Organization for Machine Automation and Control) whose state model stipulates an integrated administration of all operating modes in packaging machines. With that basis, the team will develop standard libraries for each control system and make them available to machine builders at the end of the project. Secondly, Nestlé will introduce an openSAFETY-based safety standard which is independent of the controller and bus system, and which allows for the unrestricted exchange of safetyrelated information between machines and control systems from various manufacturers.
openSAFETY
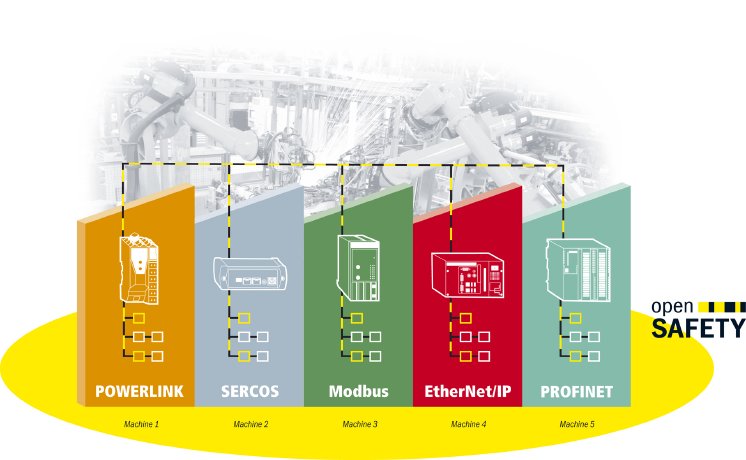
openSAFETY is a tried-and-tested safety protocol which has been certified for use in systems with a SIL 3 safety integrity level by the German testing authorities TÜV Rheinland and TÜV Süd. Highperformance safety solutions based on openSAFETY have been used in series production applications since 2008. openSAFETY is independent of the bus system and interoperable with all transport protocols thanks to the black channel principle. This means that any transport protocol can be used to transfer the safetyoriented data which is packed in a special frame format. For demonstration purposes, the POWERLINK user organization EPSG has already implemented openSAFETY for all communication systems used by Nestlé, i.e. PROFINET, SERCOS III, EtherNet/IP and POWERLINK, and additionally for Modbus TCP.
Bryan Griffen, Global Head of Electrical and Automation Engineering at Nestlé Corporate Engineering, explains openSAFETY's advantages: "Nestlé uses automation and safety components from various manufacturers. An integrated standard for safety communication allows for a reliable transfer of safety data within the complete plant, irrespective of the manufacturer of its components. Additionally, the standard also facilitates engineering with regard to system design, commissioning, and maintenance and diagnosis of the safety systems."
Company background
The Ethernet Powerlink Standardization Group (EPSG) is an independent organization founded in 2003 by leading companies from the drive and automation industry. Its aims are the standardization and further development of POWERLINK, which was first introduced by B&R in 2001. The highperformance realtime communication system is a protocol extension of the IEEE 802.3 Ethernet standard, designed to ensure realtime data transfer on the microsecond level. EPSG cooperates with leading standardization organizations, such as CAN in Automation (CiA) and the IEC. Anton Meindl, Business Manager Controls at B&R, is the EPSG's CEO.